Posterior Tibial Tendon Repair
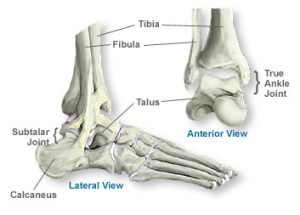 A surgeon may perform a posterior tibial tendon repair surgery for a variety of reasons including chronic inflammation or a tear of the posterior tibial tendon. A patient may tear their posterior tibial tendon during a fall, sports injury, or another ankle injury. A tear or inflammation of the posterior tibial tendon may cause the foot’s arch to drop, resulting in pain and difficulty walking requiring Flat Foot Reconstruction.
A surgeon may perform a posterior tibial tendon repair surgery for a variety of reasons including chronic inflammation or a tear of the posterior tibial tendon. A patient may tear their posterior tibial tendon during a fall, sports injury, or another ankle injury. A tear or inflammation of the posterior tibial tendon may cause the foot’s arch to drop, resulting in pain and difficulty walking requiring Flat Foot Reconstruction.
Conservative Treatment
Physicians typically attempt conservative treatment before opting for surgical intervention. Conservative treatment includes rest, ice, physical therapy, or injections. If conservative treatments do not work or the injury to the posterior tibial tendon remains too severe, then the surgeon ops for surgery.
Surgical Approach to a Posterior Tibial Tendon Repair
The surgical approach depends on the training and education of the treating physician along with the type of injury and severity of the injury. All surgeries regarding the posterior tibial tendon begin with the anesthesiologist placing the patient under general anesthesia. With the patient under general anesthesia, the patient does not feel any of the surgery and remains asleep throughout the entirety of the procedure. Due to the painful nature of the surgery, a patient may also receive a spinal nerve block to help alleviate post-operative pain.
The surgery begins with the foot and ankle surgeon making an incision through the skin and muscle of the lower calf of the leg with the affected tendon. Next, the foot and ankle surgeon makes an incision through the sheath surrounding the tendon. The surgeon then removes the damaged parts of the tendon. When removing the damaged parts of the tendon, the surgeon also removes which ever tendon they plan on using for the autograph to repair or replace the posterior tibial tendon. The graft to replace or repair the to posterior tibial tendon comes from either an allograft or autograft.
Depending on the training of the physician, the surgeon may choose to perform the posterior tibial tendon surgery using a minimally invasive approach. A minimally invasive procedure involves performing the procedure through small portals or incisions rather than large open incisions. One portal houses the camera that the surgeon views during the procedure which  allows the surgeon to see the surgical area. The surgeon uses the other portals interchangeably with tools to perform the procedure. Benefits of performing a procedure with a minimally invasive approach include lower rate of infection, less trauma to the area and surrounding tissues, and quicker recovery time.
allows the surgeon to see the surgical area. The surgeon uses the other portals interchangeably with tools to perform the procedure. Benefits of performing a procedure with a minimally invasive approach include lower rate of infection, less trauma to the area and surrounding tissues, and quicker recovery time.
To view a list of all insurances that AOA Orthopedic Specialists accept, click HERE. To schedule an appointment online, click HERE.

