DE QUERVAIN’S TENOSYNOVITIS
WHAT IS DE QUERVAIN’S TENOSYNOVITIS?
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a painful condition affecting the tendons located on the thumb side of your wrist. Do not confuse with Dupuytren’s disease. A tendon is a strong band of tissue that attaches muscle to bone. A sheath, or covering, surrounds the tendons that go to your thumb. While this sheath can commonly form ganglion cysts, tenosynovitis causes its symptoms from an irritation and inflammation of this sheath. De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis usually occurs from overusing your thumb or wrist, especially in activities that move your thumb directly away from your wrist such as skiing or hammering. This condition is more prevalent in women between the ages of 30 and 50. It is commonly associated with pain that starts in the base of the thumb that gets worse when gripping, pinching, or turning the wrist. De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis also shows some correlation with recent childbirth and the repetitive lifting motions associated with caring for a baby.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTONS OF DE QUERVAIN’S TENOSYNOVITIS?
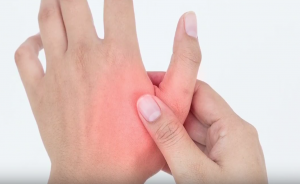 There is a test to determine if a patient has De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis that consists of making a thumbs up gesture at the ceiling for orientation. Making a fist in this position by bringing the thumb down with the fingers wrapping around it and then gently bending the hand towards the floor. If this gesture induces pain then De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis could be the cause.
There is a test to determine if a patient has De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis that consists of making a thumbs up gesture at the ceiling for orientation. Making a fist in this position by bringing the thumb down with the fingers wrapping around it and then gently bending the hand towards the floor. If this gesture induces pain then De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis could be the cause.
Symptoms of De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis include but are not limited to:
- Pain near the base of the thumb
- Swelling near the base of your thumb
- Difficulty moving your thumb and wrist when grasping or pinching
- A sticking or catching sensation in your thumb while moving it
HOW IS DE QUERVAIN’S TENOSYNOVITIS TREATED?
The treatment plan for De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is focused on reducing pain and inflammation. These treatments include:
- Applying heat or ice to the affected area
- Taking NSAIDS
- Avoiding pain and swelling causing activities i.e those that involve repetitive hand and wrist motions
- Wearing a splint
- Receiving injections of steroids or local anesthetic into the tendon sheath
If the previous listed conservative treatments do not work, surgery may be needed. The surgeon will cut a small incision in the sheath around the swollen tendons. This will provide the tendons more room to move thereby relieving the painful pressure.
IF YOU EXPERIENCE ANY HAND OR WRIST PAIN, CALL 817-375-5200 TODAY TO SCHEDULE AN APPOINTMENT!
F.A.Q.
What causes De Quervain's tenosynovitis?
The exact cause is often unknown, but repetitive hand or wrist movements, particularly those involving grabbing, pinching, or wringing motions, can contribute to the condition’s development. It is more common among women and people who engage in activities such as gardening, knitting, or working with tools.
How is De Quervain's tenosynovitis diagnosed?
A physical examination, symptom evaluation, and medical history are often used to make a diagnosis. To mimic the pain associated with the disease, the Finkelstein test, in which the thumb is bent across the palm and the wrist is flexed towards the little finger, may be done.
How long does it take to recover from De Quervain's tenosynovitis?
Many people improve within a few weeks to a few months with appropriate treatment and relaxation. The recuperation period, however, can differ based on the severity of the ailment and individual circumstances.
Can De Quervain's tenosynovitis be prevented?
While it is not always prevented, you can lower your chances of acquiring the condition by practicing appropriate ergonomics, taking pauses during repetitive activities, adopting proper hand and wrist placement, and avoiding severe thumb and wrist strain.

