Lateral Meniscus Tear
What is the lateral meniscus?
The lateral meniscus plays a very important role in the stability of your knee. Located on the outer side of the knee, the lateral meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage that attaches to the shin. It is larger and closer to a full circle than the medial meniscus and in turn covers more surface. The main purpose of the lateral meniscus is to absorb shock, lubricate the joint, and regulate the movement of the joint. It prevents the knee from going into hyper or over-extension.
types of lateral meniscus tears
Tears of the lateral meniscus are quite common. The rubbery piece of cartilage is quite susceptible to tears when the knee twists or turns in unnatural or quick movements. Degenerative tears can also occur with age or due to untreated cumulative traumas.
If a tear of the lateral meniscus occurs, it can be minor or severe. In a severe lateral meniscus tear, the meniscus can be torn in half, ripped around its circumference, or ripped to the extent that it hangs on by a fiber. Patients who suffer a tear of the lateral meniscus may have minor or moderate pain and limited movement of the knee joint. Meniscus tears present with swelling and tightness along with the inability to stretch the leg out.
The tears of the lateral meniscus are classified as:
- Longitudinal
- Radial
- Bucket Handle
- Flap
- Horizontal Cleavage
- Degenerative
Symptoms of a lateral meniscus Tear or Injury
The first clue to that you may have torn your lateral meniscus is going to be a contusion, hitting force, or energetic impact while the knee is twisting. When the knee is twisted, or twisted with a high energy impact, the meniscus can tear. When the lateral meniscus tears the patient is usually aware that something went wrong unless other trauma distracted them from the audible popping noise than many people hear and feel. However, many knee injuries also present initially with the popping noise or sensation such as a PCL or ACL tear; while knee injuries initially feel the same the situation of applied force is variable. Athletic trainers in the initial on field assessment are correct in their hypothesis 90% of the time; their recommendations are to be taken seriously.
After the initial event in which the lateral meniscus tears pain a swelling and stiffness can kick in and last weeks to months depending on the severity of additional damaged tissues from the event. After the swelling resolves the knee may feel unstable while walking and may make clicking noises during use as you push through the knee catching. It is also possible that the knee could lock or experience a reduction in range of motion. Any damage inside of the knee can result in a Baker’s cyst.
Diagnosing a lateral meniscus Tear or injury
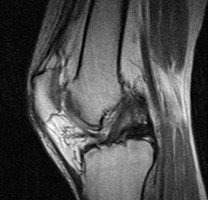
To diagnose a lateral meniscus tear, your knee specialist will perform an x-ray and MRI on the affected knee. An x-ray cannot detect a meniscus tear but it will detect other bony related conditions. An MRI is typically quite accurate in detecting a tear of the lateral meniscus.
Treating a Lateral Meniscus Tear
Depending on the size and severity of the tear, your physician will help you determine whether to proceed with conservative treatment or surgical intervention. A small or degenerative tear will most likely be treated with conservative treatments such as ice, anti-inflammatory medications, compression, and potentially a knee brace. Once swelling and pain subside, the participation in a physical therapy program may be recommended.
If conservative methods fail to sufficiently treat the knee, surgery will be required. Lateral Meniscus repair surgery is performed arthroscopically which means the surgeon will perform the surgery through 2-3 portals, or holes, in the knee. The surgeon may remove loose pieces of meniscus, cartilage, or bone floating in the joint as well. There are three options for lateral meniscus repair surgery:
- Arthroscopic repair: Using small portals made in the knee, the doctor will stitch up the tear.
- Arthroscopic partial Meniscectomy: Your doctor will remove the torn piece of the meniscus so your knee can resume normal function.
- Arthroscopic total Meniscectomy: Your doctor will remove the entirety of the meniscus.
Some unrepairable cases can consider a joint preserving meniscus transplant if the patient meets selection criteria.
F.A.Q.
What is a latrine meniscus tear?
The lateral mesicle is a C-shaped piece cartilage located in the outer portion of the knee joint. A tear in the medial meniscus can lead to pain, swelling, or restricted movement in the knee.
What is the diagnosis of a lateral meniscus tear?
To diagnose a lateral meniscus tear, a physical exam and imaging tests like an MRI are available.
What is the treatment for a lateral meniscus tear?
The treatment for a lateral tear of the meniscus depends on its size and location. Rest, ice and physical therapy can help small tears heal themselves. To repair or remove a torn meniscus, larger tears may need surgery.
How is recovery after lateral meniscus tears surgery?
Recovery times vary depending on the type and extent of surgery. Patients can resume their normal activities in a matter of months following surgery.
suspect a lateral meniscus tear?
Get Pro-sport orthopedic care today! 817-375-5200

