Subscapularis Tear
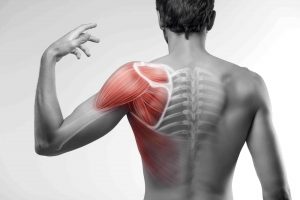 One of four muscles that make up the rotator cuff, the Subscapularis muscle originates at the subscapular fossa and inserts onto the lesser tubercle of the humerus. The largest and strongest of the rotator cuff muscles, the Subscapularis muscle consists of 60% tendon and 40% muscle. The Subscapularis muscle turns the arm inward and allows one to lift and rotate the arm. Subscapularis tears commonly occur from overuse, trauma, and age. Most trauma injuries occur from sporting events, falls, and motor vehicle accidents.
One of four muscles that make up the rotator cuff, the Subscapularis muscle originates at the subscapular fossa and inserts onto the lesser tubercle of the humerus. The largest and strongest of the rotator cuff muscles, the Subscapularis muscle consists of 60% tendon and 40% muscle. The Subscapularis muscle turns the arm inward and allows one to lift and rotate the arm. Subscapularis tears commonly occur from overuse, trauma, and age. Most trauma injuries occur from sporting events, falls, and motor vehicle accidents.
Symptoms of a Subscapularis tear
Most patients suffering from a tear of the subscapularis muscle complain of pain in the front of the shoulder. The shoulder may also make clicking or popping noises or feelings when rotating or moving the arm. The subscapularis muscle may tear alone or in tandem with other muscles of the rotator cuff, symptoms may vary depending on which muscles tear and how severely. The most commonly reported symptoms of a tear of the subscapularis muscle include:
- Pain and/or weakness of the arm or shoulder
- Increased pain when lifting the arm
- Difficulty reaching for items
- Pain underneath the collarbone
Causes of subscapularis tears
Older people may suffer a tear of the subscapularis muscle due to arthritis or degeneration that occurs with age. In younger individuals, subscapularis tears typically occur due to injury or trauma. Sporting events commonly cause tears to the subscapularis muscle along with the other muscles of the rotator cuff. Traumatic events like falls or car accidents also often cause tears of the subscapularis muscle.
Diagnosing and Treating Subscapularis tears
When suspecting an injury to the shoulder, patients should seek out the expertise of a board certified shoulder physician. First the physician conducts a physical examination and goes over medical history with the patient. The doctor may perform a variety of physical “tests” including the lift-off test, bear hug test, and belly press test. If the doctor suspects a tear to the subscapularis or any shoulder muscle, the physician orders an MRI to confirm the suspicion. The doctor may also perform an ultrasound.
If the physician finds a tear in the subscapularis muscle, treatments depends on the size of the tear and the patients lifestyle. With a small tear in an older individual with a relatively sedentary lifestyle, the treating doctor may 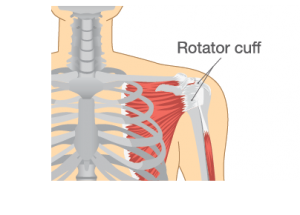 recommend conservative treatments. Conservative treatments typically include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and potentially steroid injections.
recommend conservative treatments. Conservative treatments typically include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and potentially steroid injections.
In a younger patient, highly active patient, or a patients with a full thickness tear of the muscle, the physician most likely recommends surgery to repair the tear. In most cases, the surgeon performs the surgery arthroscopically, but in certain instances the surgeon may need to make a larger incision.
To view a list of all insurances that AOA Orthopedic Specialists accept, click HERE. To schedule an appointment online, click HERE.
EXPERIENCING shoulder PAIN? CALL 817-375-5200 TO SCHEDULE AN APPOINTMENT WITH AN AOA ORTHOPEDIC SPECIALIST TODAY!
F.A.Q.
What is a Subscapularis Tear?
A Subscapularis Tear is a type of rotator cuff injury that affects the subscapularis muscle, one of the four muscles that make up the rotator cuff in the shoulder. This tear occurs when the subscapularis muscle or its tendon is damaged or partially torn. It can result from overuse, trauma, or the natural aging process and may cause pain, weakness, and limited range of motion in the shoulder.
What are the common symptoms of a Subscapularis Tear?
Common symptoms of a Subscapularis Tear include shoulder pain, especially in the front or deep within the shoulder joint. You may also experience weakness in the affected shoulder, making it challenging to perform everyday tasks like lifting or reaching. In some cases, individuals may notice a clicking or popping sensation when moving the shoulder, and they may have difficulty rotating the arm.
How is a Subscapularis Tear diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and imaging studies, such as MRI or ultrasound, to assess the extent of the tear. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the tear. Conservative treatments like rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications are often recommended for mild to moderate tears. For more severe tears, surgical repair may be necessary. Our experienced orthopedic specialists will assess your condition and develop a personalized treatment plan to help you recover and regain shoulder function.

